


I have found a website that is very helpful in identifying the pins of optical encoder from the printer:
X4 – if we count each rising edge and falling edge of both Channel A and Channel B, we’ll get 4 pulses per cycle, or 1782 x 4 = 7128 pulses per revolution ( 7128PPR). X2 – if we count each rising edge and each falling edge of Channel A, we’ll get 2 pulses per cycle, or 1782 x 2 = 3564 pulses per revolution ( 3564PPR). X1 – if we count the rising edge of each Channel A pulse, we’ll get 1 pulse per cycle or 1782 pulses per revolution ( 1782PPR). Picture below summarizes the quadrature function of optical encoder:įor example, we consider a 1782CPR rotary optical encoder - Y axes of Dell printer as described in previous step: When X4 encoding is used, it increases encoder resolution by four times. X4 encoding: both the rising and falling edges of channels A and B are counted. When X2 encoding is used, it increases encoder resolution by two times. X2 ENCODING X2 encoding: both the rising and falling edges of channel A are counted. When channel B is leading, the movement is considered as counterclockwise or backward, and the count number is decreased.Ģ. X1 encoding: the rising or the falling edge of channel A is counted. We can increase encoder’s resolution by counting the rising and falling edges of two channels, detail is explained below. When it moves/ rotates in a forward/ clockwise direction, channel A leads channel B, and in case it moves/ rotates in backward/ counterclockwise direction channel B leads channel A. But for quadrature encoder, it produce two channels, named channel A and channel B. With a single output encoder, it has no way of detecting in which direction the motion is happening. The two output channels from an encoder, with one being offset by 90 electrical degrees, or one quarter of a cycle that usually called quadrature encoder. The optical encoder is widely used due to its low cost and ability to provide signals that can be easily interpreted to provide motion related information such as speed or position. High LPI indicates greater detail and sharpness. Lines per inch ( LPI) is a measurement of printing resolution. In the case of rotary encoders, resolution is specified as the cycles per revolution ( CPR), some manufacturers use terms like “ counts per revolution” (also abbreviated CPR) or pulses per revolution ( PPR). Optical sensor and control board: It is not clear, part number maybe J15 (0947). OPTICAL ENCODERS: There’re 2 kinds of optical encoders in DELL printer as follows: I only saw two DC motors equivalent to my printer motors, as follows:Ģ. But I could not find out the specifications of these motors on MABUCHI MOTOR website according to the order number written on the motors body. Through my searches on internet, perhaps these motors belong to the MABUCHI MOTOR manufacturer. DC MOTORS: There're 2 DC motors for X & Y axis as follows: 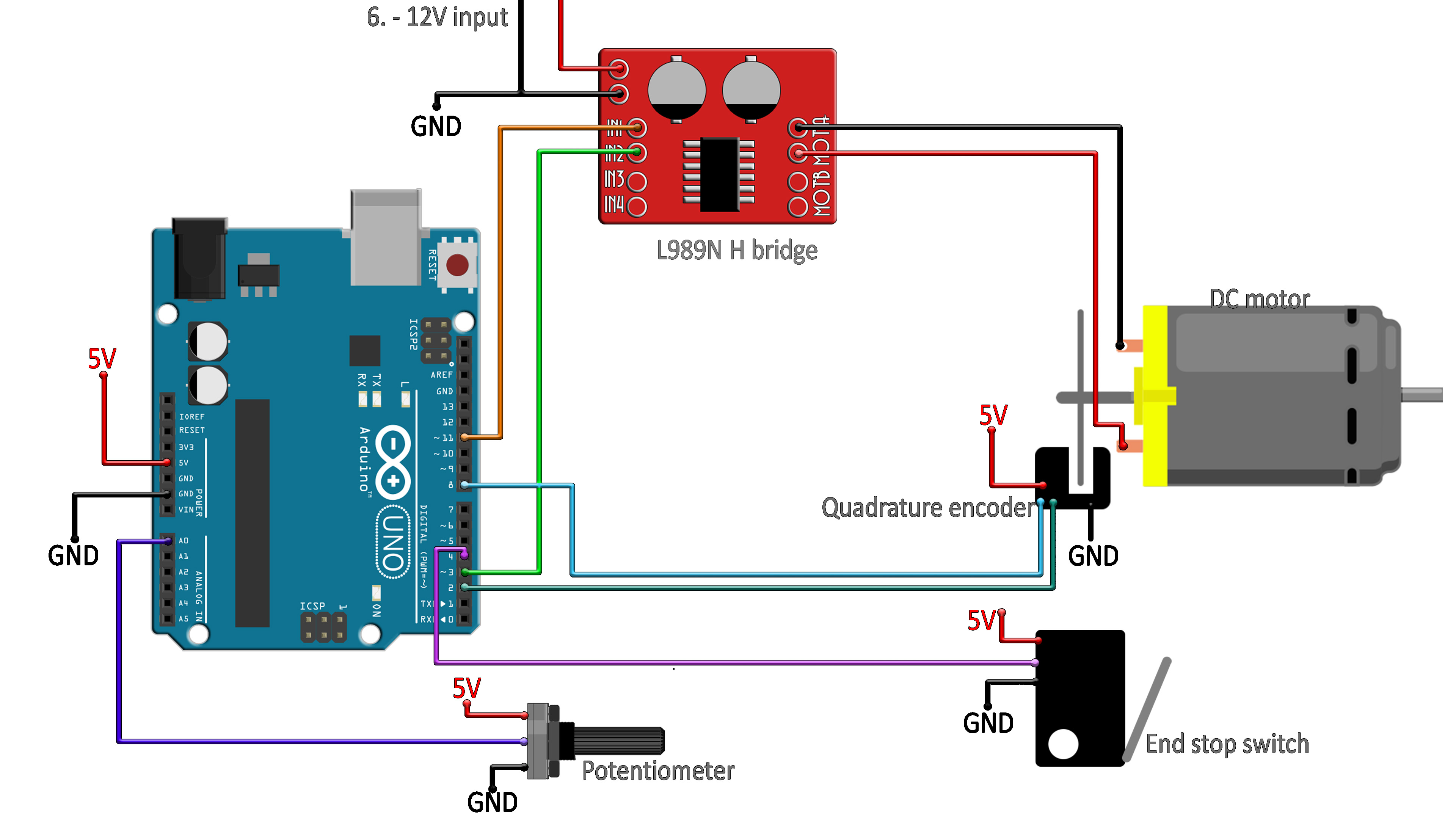
ĭetails of printer components are described below:ġ. 1pcs x Aluminum Flexible Shaft Coupling, Inner Hole Size: 10mm x 10mm.2pcs x Male & Female 40pin 2.54mm Header.2pcs x 2.54mm Pitch 40 Long Pin Single Stackable Shield Female Header.1pcs x Single/ Double Sided Printed Prototyping Board.2pcs x XH2.54mm – 2P 20cm Wire Cable Double Connector.2pcs x XH2.54mm – 4P 20cm Wire Cable Double Connector.1pcs x Old CD/DVD Burner Writer Rom Player Drive.I used old printer head frame from DELL printer, one optical encoder is linear type and the other is rotary type.
POSITION CONTROL OF A DC MOTOR ARDUINO PLUS
1pcs x Old Printer Head Frame with 2 DC motors plus their optical encoders.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
